Extending integrations
Introduction
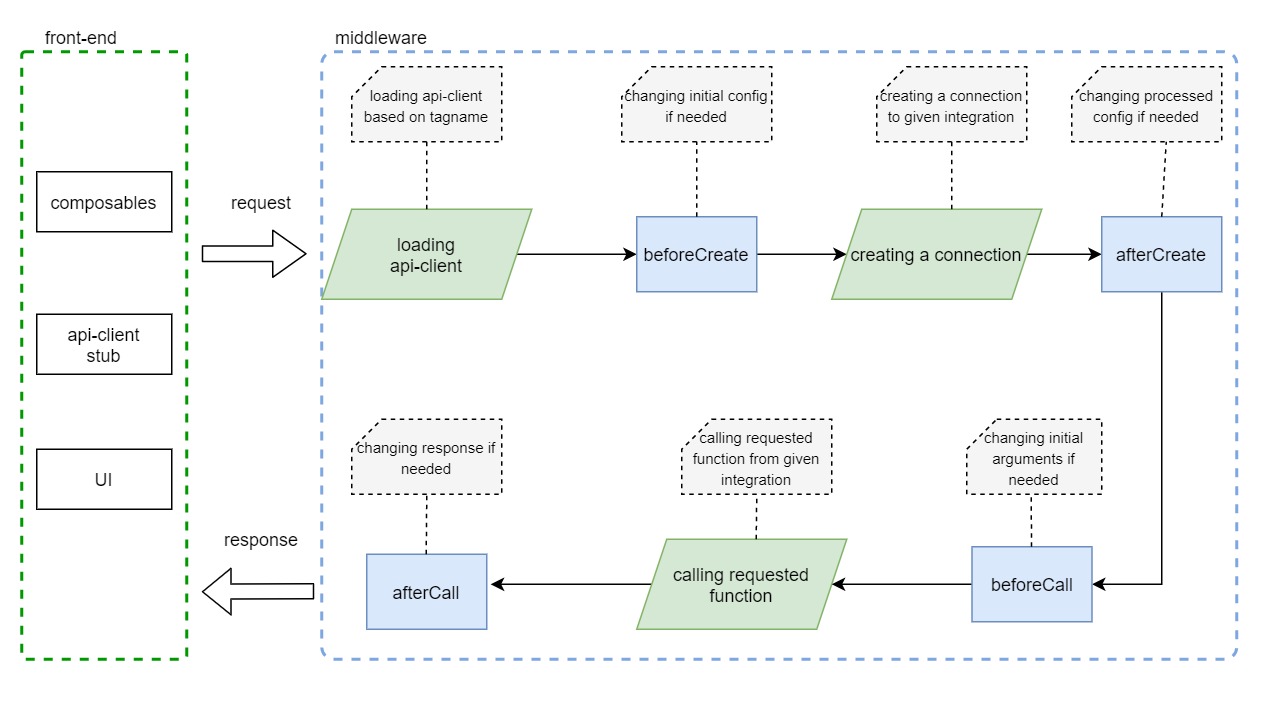
Server Middleware extensions allow to extend Express.js server, register additional API endpoints, or inject into the lifecycle of a request sent to a given Server Middleware integration from the application.
Creating an extension
You can define as many extensions as you want. Each extension has the following structure:
const extension = {
name: 'extension-name',
extendApiMethods: {
customMethod: (context, params) => { /* ... */ },
},
extendApp: ({app, configuration}) => { /* ... */
},
hooks: (req, res) => {
return {
beforeCreate: ({ configuration }) => configuration,
afterCreate: ({ configuration }) => configuration,
beforeCall: ({ configuration, callName, args }) => args,
afterCall: ({ configuration, callName, args, response }) => response
}
}
}
name- defines the unique name of the extensionextendApiMethods- overrides the original functions from API-clientextendApp- a function that gives you access to the express.js apphooks- defines lifecycle hooks of API-clienthooks:beforeCreate- called before API-client creates a connection. It accepts configuration as an argument, and must return it as well. You can use it to modify the configuration or merge with the default values.hooks:afterCreate- similar to the previous function, but called after the connection has been created. It accepts configuration as an argument, and must return it as well.hooks:beforeCall- called before each API-client function. We have access to the configuration, function name, and its arguments. This function must return the arguments, and based on the input parameters we can change it.hooks:afterCall- called after each API-client function. We have access to the configuration, function name, and its arguments. This function must return the response, and based on the input parameters we can attach something to it.
See the ApiClientExtension interface for more information.
Registering an extension
To register an extension, add it to the array returned from the extensions function of a given integration in
the middleware.config.js file:
module.exports = {
integrations: {
'{INTEGRATION_NAME}': {
// ...
extensions: (extensions) => [
...extensions,
{
name: 'extension-name',
hooks: () => { /* ... */ }
}
]
}
}
};
Example: Adding new API endpoints
To register a new API endpoint, you can register a custom extension and use the extendApiMethods property. API
endpoints cannot be registered directly. Let's look at an example:
module.exports = {
integrations: {
'{INTEGRATION_NAME}': {
// ...
extensions: (extensions) => [
...extensions,
{
name: 'extension-name',
extendApiMethods: {
customMethod: async (context, params) => {
const response = await context.client.mutate({
mutation: gql`${someQuery.query}`,
variables,
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache', // in most cases you do not want to cache response in the Apollo
/**
* This is a required object and must be attached to every graphql endpoint
* with req and res node objects inside.
* If you are using custom client then you can omitt this.
*/
context: {
req: context.req,
res: context.res
}
});
}
}
}
],
}
}
};
Because this is an abstract example that applies to all integrations, we intentionally used {INTEGRATION_NAME} as the
name of the integration. In this example, we are registering customMethod in extendApiMethods that creates a
new /api/{INTEGRATION_NAME}/customMethod endpoint.
This method accepts two parameters:
contextwhich includes:config- integration configuration,api- integration endpoints exposed as methods,client- API client created inpackages/api-client/src/index.server.ts,req- HTTP request object,res- HTTP response object,extensions- extensions registered within integration,customQueries- custom GraphQL queries registered within integration (used only with GraphQL),extendQuery- helper function for handling custom queries (used only with GraphQL).
params- parameters passed.
You can call this endpoint from the application like so:
import { useVSFContext, onSSR } from '@vue-storefront/core';
export default {
setup() {
const { $INTEGRATION_NAME } = useVSFContext();
onSSR(async () => {
await $INTEGRATION_NAME.api.customMethod({
query: 'test',
limit: 20
})
});
}
}
This will send a POST request, similar to this one:
curl '{SERVER_DOMAIN}/api/INTEGRATION_NAME/customMethod`' \
-X POST \
-H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '[{"query":"test","limit":20}]'